Ever wonder why a specific piece of music makes your heart ache, or sends a jolt of pure joy through your system? It's not just the melody or the rhythm; often, the silent architect of these powerful reactions is Chord Progression Psychology. This fascinating field explores how the sequence of chords in a song profoundly shapes our emotional landscape, playing on our expectations and delivering a symphony of human feeling directly to our brains.
From the stirring build of a movie soundtrack to the comforting familiarity of a pop hit, chord progressions are the hidden language that speaks to our deepest emotions. Let’s decode how this musical magic happens.
At a Glance: How Chords Play on Your Emotions
- Brainwired Responses: Our brains predict musical harmony, creating tension and release that trigger satisfaction or surprise.
- Cultural Context: We learn to interpret musical "grammar" based on our culture and personal experiences.
- Dopamine Rush: Certain chord sequences activate the brain's reward system, releasing dopamine and creating pleasure.
- Major vs. Minor: Major chords generally signal happiness and optimism; minor chords evoke sadness and introspection.
- Tension & Release: Dissonant or unexpected chords build tension, which is then resolved by consonant or predictable ones, creating emotional journeys.
- Composer's Toolbox: Composers deliberately use key choices, inversions, borrowed chords, and even unconventional progressions to craft specific emotional impacts.
- Interplay with Other Elements: Chords work with melody, rhythm, instrumentation, and lyrics to create a complete emotional picture.
The Silent Language of Our Souls: What is Chord Progression Psychology?
At its heart, Chord Progression Psychology investigates the intricate dance between sound, structure, and human emotion. It's about understanding why a simple shift from a major to a minor chord can dramatically alter the entire feeling of a piece, transforming a sunny tune into a somber reflection in an instant.
Our brains aren't just passive recipients of music; they're active participants, constantly making predictions about what comes next. When a chord progression unfolds, our neural pathways are busy at work, anticipating the next harmonic step. The interplay between these expectations and the actual musical resolution – or lack thereof – is what generates our feelings of satisfaction, tension, surprise, or even confusion.
Think of it like a story: you anticipate a happy ending, but then there's a twist. The emotional impact comes from how that twist is delivered and ultimately resolved. Music works similarly, with each chord acting as a plot point in a sonic narrative. These neural responses are deeply influenced by our cultural background and personal experiences, as we unconsciously internalize our culture's musical "grammar" from a young age. Research even indicates that certain chord progressions activate the brain's reward system, releasing dopamine and inducing profound feelings of pleasure. It's a fundamental part of what makes music so universally captivating.
Why Do These Chords Make Me Feel That Way? The Emotional Lexicon of Harmony
Not all chords are created equal when it comes to emotional impact. Different types of chords and their specific sequences have developed strong, often universal, associations with various feelings.
Major and Minor: The Foundation of Feeling
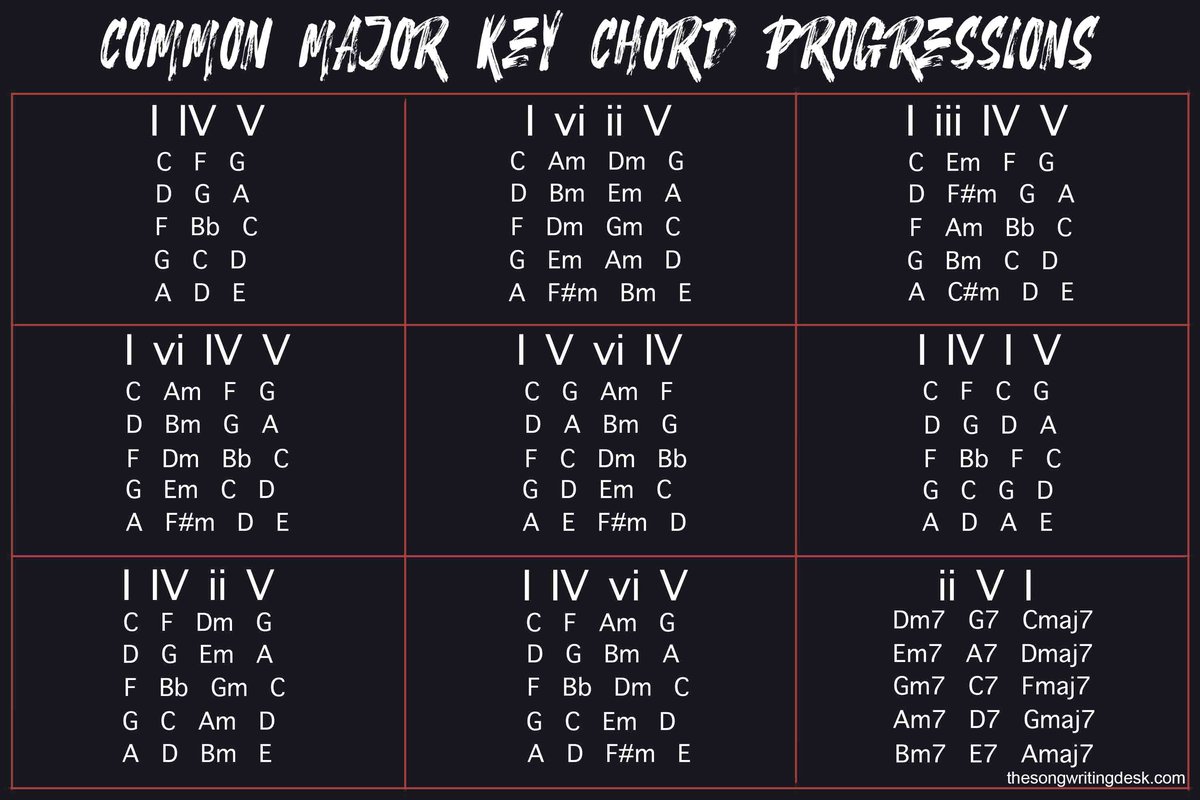
- Major Chords: These are the sunny optimists of the musical world. Associated with happiness, optimism, resolution, and uplift, major chords often provide a sense of stability and joy. Think of many children's songs or triumphant movie scores – they’re brimming with major progressions. A classic example is the I-V-vi-IV progression (e.g., C-G-Am-F in C Major), which has been the bedrock of countless pop anthems, known for its feel-good, resolute quality.
- Minor Chords: Step into the realm of introspection, melancholy, and longing with minor chords. While not always "sad," they often evoke a sense of seriousness, drama, or contemplation. They pull us into deeper emotional landscapes, prompting reflection. The i-iv-v progression (e.g., Am-Dm-Em in A Minor) is a quintessential example, frequently used to convey a sense of pathos or yearning.
Diminished and Augmented: Stirring the Pot
Beyond the major and minor, other chord types are specialists in specific emotional effects:
- Diminished Chords: These chords are masters of tension and uncertainty. They sound unstable, yearning to resolve somewhere, anywhere. They're often used to create suspense, unease, or a sense of foreboding, acting as a dramatic pause before a resolution.
- Augmented Chords: If you want surprise and drama, augmented chords are your go-to. They sound a bit "wonky" or "floaty," defying easy resolution and creating an ethereal, often unsettling, or dreamlike quality. They can be used to add a touch of the fantastical or the bizarre.
The Push and Pull: How Tension and Release Play on Our Minds
One of the most powerful psychological tools in a composer's arsenal is the interplay of tension and release. It’s a core principle of how music evokes emotion. Imagine holding your breath, then finally exhaling – that's the musical equivalent.
Tension is often achieved through dissonant or unexpected chord progressions. These chords create a sense of unease, a feeling that something is "wrong" or "unfinished." Our brains, wired for predictability, sense this harmonic instability and anticipate a resolution. When that resolution comes, usually in the form of a consonant or predictable chord, we experience a feeling of satisfaction, relief, or emotional catharsis. This dynamic can be mathematically represented by concepts like harmonic entropy, where less predictable, more "disordered" harmony creates tension.
Unexpected chord changes, in particular, are potent emotional triggers. They can evoke:
- Surprise: A sudden, delightful turn that wakes up the listener.
- Wonder: A sense of awe and curiosity, often leading to a feeling of expansiveness.
- Confusion: When the progression goes somewhere truly unexpected, challenging our internal musical grammar.
- Humor: In some contexts, a jarring or silly chord change can even be laugh-out-loud funny.
This constant dance between expectation and surprise, tension and release, is what keeps us engaged and makes music a profound emotional journey rather than a static sound.
The Composer's Toolkit: Crafting Emotional Journeys with Chords
Composers don't just stumble into emotional chord progressions; they craft them with intention. It's a deliberate art form, much like a chef carefully selecting ingredients.
Starting with Emotion and Key
- Identify the Target Emotion: Before anything else, a composer determines the desired feeling. Do they want to evoke joy, sadness, anger, mystery, or longing? This emotional goal guides every subsequent chord choice.
- Choose Key and Mode: The foundational choice of key and mode sets the overall emotional tone. As we discussed, major keys tend to sound happier and more stable, while minor keys lean towards sadness, introspection, or tension. Beyond these, modes like Dorian can add a touch of mystery or wistfulness, while Phrygian can sound exotic or dark.
Beyond the Basics: Inversions and Borrowed Chords
- Utilize Chord Inversions: A seemingly small change can have a big emotional impact. Chord inversions – where the notes of a chord are rearranged so that a note other than the root is in the bass – can add subtle emotional nuance. For example, a root position chord might sound grounded, while a first inversion might feel lighter or more suspended.
- Incorporate Non-Diatonic Chords: To introduce tension, surprise, beauty, or complexity, composers often step outside the "home key" using non-diatonic chords. These "outside" chords create harmonic friction, making the listener lean in and pay attention, often leading to a more satisfying resolution when the music returns to the expected harmony.
- Employ Modal Interchange: This sophisticated technique involves borrowing chords or scales from parallel modes or keys (e.g., taking a chord from C minor and using it in C major). Modal interchange is a powerful way to create variety and unexpected emotional shifts without fully modulating to a new key. It allows for a momentary darkening or brightening of the mood, adding layers of emotional depth.
Daring to Be Different: Unconventional Progressions
- Experiment with Unconventional Progressions: For truly unique emotional landscapes, composers might use altered dominants, unusual voicings, or entirely unexpected chord juxtapositions. These can challenge the listener's expectations, leading to feelings of wonder, confusion, or even abstract beauty that pushes the boundaries of traditional harmony. This is where innovation sparks, creating sounds never heard before. If you're looking to dive deeper into how chords ignite innovation, you might find Your complete guide to sparks chords particularly illuminating.
More Than Just Chords: The Orchestra of Emotion
While chord progressions are profoundly powerful on their own, their emotional impact is rarely experienced in isolation. They interact with other musical elements, creating a rich tapestry of feeling.
- Melody: The melody is often the emotional narrator, and it works hand-in-hand with the chord progression. The melody can enhance the emotional message of the chords (e.g., a sad melody over minor chords) or, intriguingly, subvert it (e.g., a hopeful melody over somber chords, creating a sense of bittersweetness).
- Rhythm: The rhythmic pulse of a piece sets the emotional pace. Fast, driving rhythms can add urgency and excitement to a progression, while slow, languid rhythms can amplify melancholy or create a sense of relaxation, even with the same set of chords.
- Instrumentation and Timbres: The instruments chosen and their unique sound qualities (timbre) significantly affect how chord progressions are perceived. A minor progression played on a solo cello will evoke a different feeling than the exact same progression played by a distorted electric guitar or a choir. The warmth of a string section versus the piercing quality of a trumpet can completely alter the emotional weight of the harmony.
- Lyrics: In songs with words, lyrics interact directly with chord sequences. The chords can reinforce the emotional message of the words (e.g., a heartbreaking lyric with a poignant minor progression) or, by contrast, create dramatic irony or a more nuanced emotional experience (e.g., an angry lyric sung over a surprisingly gentle progression).
Genre by Genre: How Music Styles Harness Chordal Power
Different musical genres employ chord progressions in unique and characteristic ways, reflecting their aesthetic goals and the emotional palettes they aim to explore.
- Classical Music: Often utilizes complex harmonic structures to craft intricate, evolving emotional journeys. Composers like Beethoven or Wagner could build immense tension and profound resolution over many minutes, using sophisticated voice leading and harmonic modulations to tell epic sonic stories.
- Pop Music: Frequently relies on familiar, archetypal chord progressions for comfort, satisfaction, and nostalgia. The emphasis is often on immediate emotional accessibility and catchiness, using progressions that reliably trigger positive or relatable feelings, such as the aforementioned I-V-vi-IV, which has become a pop staple for its uplifting and memorable quality.
- Jazz: Embraces extended chords, altered harmonies, and sophisticated substitutions for complex, nuanced emotional landscapes. Jazz progressions are often designed to surprise, delight, and challenge the listener, creating rich textures and unexpected turns that evoke a sense of sophisticated wonder or cool melancholy.
- Electronic Music: Explores unconventional progressions, often leveraging synthetic sounds and unique rhythmic patterns to create unique and sometimes unsettling, otherworldly, or highly abstract emotional palettes. It can push boundaries, creating feelings of disorientation, euphoria, or intense contemplation that are distinct from more traditional genres.
Decoding the Masters: Learning from the Greats
For aspiring composers, musicians, or even just curious listeners, analyzing famous compositions can provide invaluable insights into Chord Progression Psychology. Take, for instance, Chopin's Nocturne in E-flat major (Op. 9, No. 2). While primarily in a major key, conveying a dreamy, lyrical quality, Chopin masterfully weaves in both diatonic and non-diatonic chords. He introduces moments of gentle tension with chromaticism and then resolves them gracefully, creating a continuous ebb and flow of poignant beauty and serene contentment. Listening to how he uses these subtle harmonic shifts to paint a rich emotional picture is a masterclass in itself.
When you're providing feedback on a composition or simply trying to deepen your appreciation, ask yourself:
- Does the chord progression evoke the intended emotion? Does it feel joyful, somber, tense, or resolved as the composer likely intended?
- Are the moments of tension and resolution effective? Do they grab your attention and then provide a satisfying release?
- How does the progression contribute to the overall mood and narrative of the piece? Is it consistent, or does it offer intriguing contrasts?
Your Turn: Applying Chord Progression Psychology (Whether You Listen or Compose)
Whether you're a seasoned musician, an aspiring songwriter, or simply someone who loves to get lost in music, understanding Chord Progression Psychology enhances your experience.
For Listeners:
- Active Listening: Don't just hear the melody; pay attention to the underlying harmony. Can you distinguish between major and minor sections? Do you notice when a chord feels "tense" or "resolved"?
- Emotional Mapping: Connect the specific chord changes you hear to the emotions they evoke in you. Does a particular shift consistently make you feel a certain way?
- Genre Exploration: Explore how different genres use harmony to achieve their signature emotional impact. Listen to classical pieces for intricate journeys, pop for comfort, jazz for nuance, and electronic for unique textures.
For Composers and Musicians: - Start with Emotion: Always begin by defining the emotional core of your piece. This will guide your harmonic choices.
- Experiment Beyond the Obvious: Don't be afraid to step outside the basic major/minor toolkit. Introduce diminished chords for suspense, augmented chords for surprise, or non-diatonic chords for unexpected beauty.
- Focus on Tension and Release: Consciously build and release tension. Think about how you want to guide your listener through an emotional arc. Where do you want to create unease, and where do you want to provide comfort?
- Listen Critically: Analyze your own work and the work of others with an ear for harmonic psychology. Does your chord progression truly convey what you intend, or could a slight alteration deepen its impact?
Quick Answers: Unpacking Common Questions About Chords and Feelings
Q: Are certain chord progressions universally emotional, regardless of culture?
A: While there are strong cross-cultural tendencies (e.g., major = happier, minor = sadder), particularly in relation to tension and release, the specific nuance of those emotions and their intensity can be culturally mediated. Our brains internalize the musical "grammar" of our upbringing.
Q: Can a "happy" chord progression be used to convey sadness?
A: Absolutely! This is where the interaction with other musical elements becomes crucial. A major progression with a slow tempo, a melancholic melody, and somber instrumentation (e.g., a cello) can create a deeply bittersweet or wistful feeling, playing on the contrast.
Q: How do composers avoid sounding repetitive with common progressions?
A: Composers use various techniques, including reharmonization (changing chords under a familiar melody), inversions, modal interchange, varying instrumentation, rhythmic alterations, and adding non-diatonic "spice" to familiar structures, keeping the emotional journey fresh.
Q: Is there a "formula" for writing emotionally impactful chord progressions?
A: While there are common patterns and psychological principles, music is an art. There's no rigid formula, but rather a set of tools and techniques that, when applied with intention and creativity, can lead to powerful emotional results. Understanding the why behind the tools is key.
The Unseen Symphony: Embracing the Emotional Power of Chords
The next time you find yourself moved by a piece of music, pause and consider the silent, unseen symphony unfolding beneath the surface. It's the sophisticated dance of Chord Progression Psychology at play, a testament to the profound connection between organized sound and the human heart. By understanding how these harmonic sequences stir our feelings, you gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry behind the music and the incredible way our brains are wired to respond to its magic. Go forth, listen, and let the chords speak to your soul.